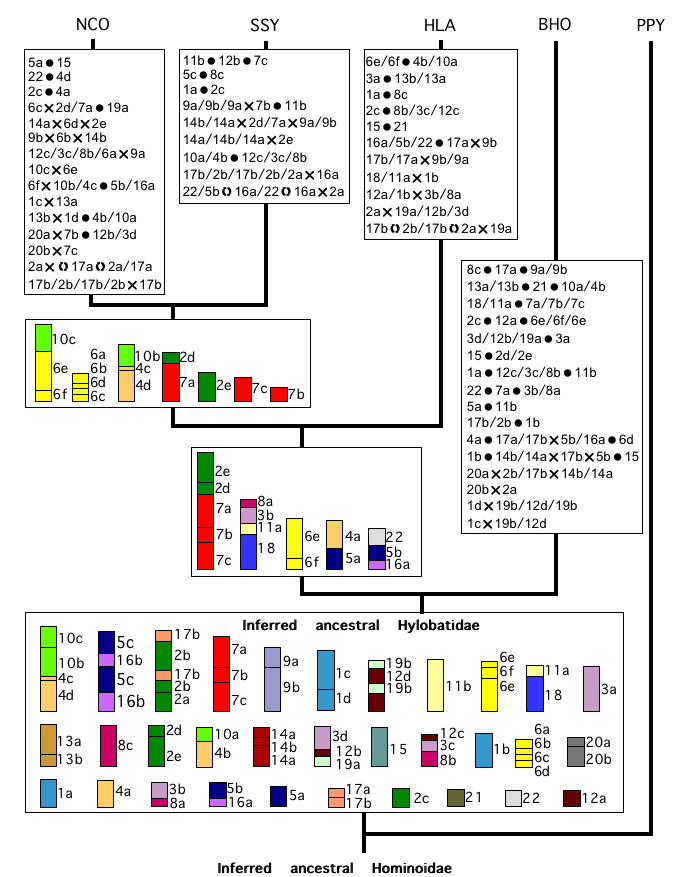
Gibbons have extremely derived karyotypes ("chromosome reshuffling“). Rearrangements include reciprocal translocations, fissions, fusions and inversions.
Data from:
N. concolor: Müller et al. 1998; Rens et al. 2001
B. hoolock: Yu et al. 1997; Nie et al. 2001
H. lar: Jauch et al. 1992; Müller et al. 2002
S. syndactylus: Koehler et al. 1995; Müller et al. 2003
The inferred ancestral gibbon karyotype differs from the putative hominoid ancestor by a minimum of 24 rearrangements (7 reciprocal translocations, 7 inversions and 10 fissions)
Several rearrangements are species-specific (approximately 10 in H. lar and 21 in B. hoolock).
PAUP (Phylogenetic Analysis using Parsimony): PPY[BHO[HLA[SSY/NCO]
